专业丛书
U.S. Trust and Estate Planning 美國信託規劃實務(英文部分)
Chapter 5 The Rise of the Global Family Office
A Family Office is a private wealth advisory entity established by an individual or family to manage wealth and provide a variety of personal and financial services. Family Offices serve high-net-worth individuals and families, offering a comprehensive approach to managing their financial affairs and providing services beyond traditional wealth management.
A Family Office is a private wealth advisory entity established by an individual or family to manage wealth and provide a variety of personal and financial services. Family Offices serve high-net-worth individuals and families, offering a comprehensive approach to managing their financial affairs and providing services beyond traditional wealth management. Family Offices typically provide some, if not all, of the following services:
In essence, a Family Office acts as a centralized entity that coordinates and manages all aspects of a family’s wealth, aiming to preserve and grow their wealth while providing a suite of bespoke services to meet their unique needs.
1. Wealth Management:
-
- Investment management, asset allocation, and risk management.
- Property management, rent collection and lease renewals.
- Developing and implementing investment strategies aligned with the family’s goals and risk tolerance.
2. Tax Services:
-
- Tax planning and compliance.
- Tax risk mitigation and analysis.
- Strategies to minimize tax liabilities and maximize tax efficiency.
3. Legal Services:
-
- Estate planning, including the creation of wills and trusts.
- Legal advice on establishing and managing closely held family businesses.
4. Succession Planning:
-
- Developing plans for the transition of wealth and business to the next generation.
- Ensuring the continuity of family values and objectives.
5. Risk Management:
-
- Evaluating and managing risks associated with the family’s assets and activities.
- Managing the family’s risk exposure to various incidents and investments.
6. Insurance Management
-
- Comparing, procuring and managing insurance policies.
- Planning for liquidity to pay estate taxes and other expenses, ensuring that the estate can pass to heirs without being diminished.
7. Administrative Services:
-
- Handling day-to-day administrative tasks, such as bill payments, financial reporting, bookkeeping, and record-keeping.
- Managing household staff and personal affairs.
8. Lifestyle Management:
-
- Personal services such as travel arrangements and luxury purchases.
- Assistance with health and wellness, education, and other personal needs.
9. Philanthropy
-
- Providing advice on philanthropy, charitable giving, and legacy planning.
(A) Customization: Tailored solutions that align with the family’s specific needs and goals.
(B) Control and Privacy: Greater control over investments and decision-making, with a high level of privacy.
(C) Holistic Approach: Integration of various aspects of wealth management, from investments to lifestyle services, under one roof.
(D) Long-Term Planning: Focus on long-term wealth preservation and intergenerational transfer.
In essence, a Family Office acts as a centralized entity that coordinates and manages all aspects of a family’s wealth, aiming to preserve and grow their wealth while providing a suite of bespoke services to meet their unique needs.
Wealth Creators with considerable net worth should also consider establishing a U.S. family trust (the types and steps have been described at length in previous chapters). When establishing a familial trust, the family’s Family Office is particularly important. A properly staffed Family Office, for the purposes of establishing a trust, should include:
- A U.S. Trust Attorney, who typically drafts the trust agreement.
- A U.S. Tax Attorney, who typically analyzes the tax effect of the family trust.
- A U.S. Certified Public Accountant (CPA), who can complete and submit applicable and required U.S. tax forms and disclosures.
- A Local Certified Public Accountant (CPA), who resides in the Grantor’s resident country and can analyze the local tax effects of establishing a U.S. trust.
- A Local Attorney, who can analyze the legal ramifications of transferring certain assets into a U.S. trust in the Grantor’s resident country.
- A Compliance Secretary, who can manage the transfer of funds from Asia to the U.S. along with any required Know-Your-Client (KYC) paperwork.
- A Specialized Secretary, who can manage offshore companies (typically established in the British Virgin Islands (BVI) or the Cayman Islands).
- One or more Financial Advisors, who can manage investments in Asia and in the U.S.
- A United States trust company that is able and willing to act as trustee of a family trust. United States Trust Company, which mainly serves Chinese, should preferably have Chinese communication skills; All trust establishment documents (including trust contracts) can be provided in both English and Chinese; The trust professionals are also bilingual in English and Chinese, so as not to misunderstand the meaning of family trust.
Since the process of establishing a family trust typically can take anywhere from 6 months to several years, it is extremely important that all parties maintain open communication and are synced to the client’s particular needs and circumstances.
A Single-Family Office (SFO) and a Multi-Family Office (MFO) are both entities designed to manage the wealth and financial affairs of families, but they differ in structure, clientele, and the range of services offered. Here are the key differences:
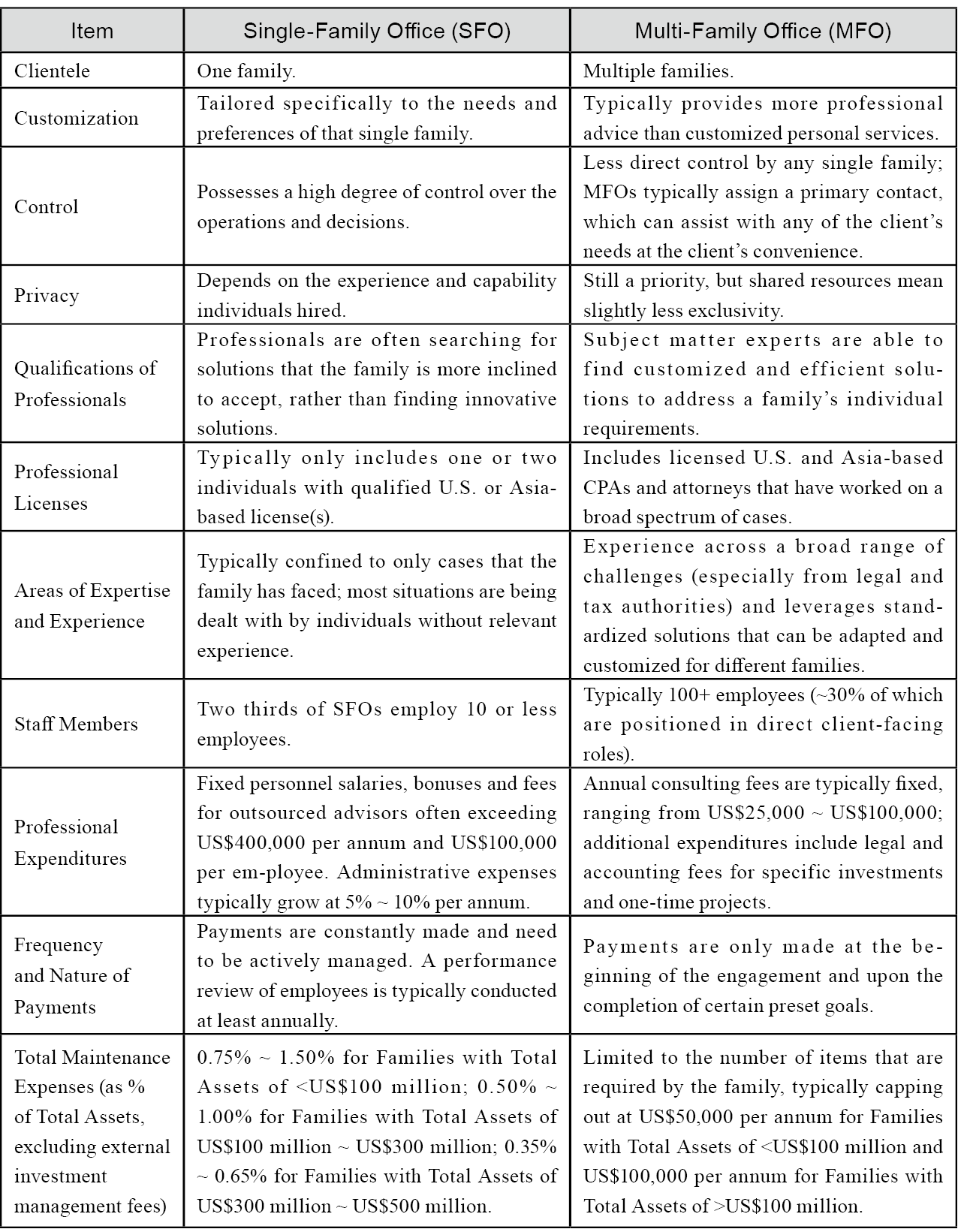
In essence, the primary difference lies in the number of families served, the level of personalization, the proficiency of entity employees, and the total annual operating expenses. A Single-Family Office is highly bespoke, while a Multi-Family Office leverages economies of scale to provide cost-effective yet comprehensive services to multiple families.

In essence, the primary difference lies in the number of families served, the level of personalization, the proficiency of entity employees, and the total annual operating expenses. A Single-Family Office is highly bespoke, while a Multi-Family Office leverages economies of scale to provide cost-effective yet comprehensive services to multiple families.
Selecting a Multi-Family Office (MFO) is a critical decision for high-net-worth families. Here are the most important criteria to consider:
1. Reputation and Track Record:
-
- Reputation: Research the MFO’s reputation within the industry. Look for reviews, testimonials, and any potential red flags.
- Track Record: Evaluate the MFO’s history of performance. This includes their success in managing wealth, client satisfaction, and the stability of their client relationships over time.
2. Services Offered:
-
- Comprehensive Services: Ensure the MFO offers a wide range of services, including investment management, tax planning, estate planning, risk management.
- Customization: Assess their ability to tailor services to meet the specific needs of your family.
3. Expertise and Experience:
-
- Professional Team: Evaluate the qualifications and experience of the MFO’s team. This includes financial advisors, tax experts, legal advisors, and other professionals.
- Specialization: Consider whether the MFO has experience working with families with similar financial profiles and needs.
- International Exposure: Cross-border families should pay special attention to the firm’s past experience with cross-border tax and estate planning.
4. Philosophy and Strategy:
-
- Alignment: Ensure the MFO’s philosophy align with your family’s goals, risk tolerance, and values.
- Asset Class: Evaluate whether the MFO has experience working with your family’s preferred investments, especially if your family has a large position in a particular asset class.
5. Transparency and Communication:
-
- Reporting: Check the frequency and clarity of financial reporting. Transparent, regular reports are crucial for tracking performance and making informed decisions.
- Communication: Evaluate the MFO’s communication practices. They should be accessible, responsive, and proactive in keeping you informed.
6. Fees and Cost Structure:
-
- Fee Structure: Understand the fee structure and ensure it is transparent. These often include annual consulting fees and itemized service charges. Certain MFOs may also charge a fee as a percentage of total assets or assets under management.
- Value for Money: Assess whether the services provided justify the costs. Compare the fee structures of different MFOs.
7. Client-to-Advisor Ratio:
-
- Attention: A lower client-to-advisor ratio generally means more personalized attention and better service.
- Accessibility: Ensure your family will have sufficient access to advisors and their support.
8. Cultural Fit and Trust:
-
- Cultural Fit: Ensure the MFO’s culture and values align with your family’s. This includes their approach to wealth management and client relations.
- Trust: Building a trusting relationship is crucial. You should feel confident in their ability to manage your resources and act in your best interests.
9. Technology and Innovation:
-
- Technology: Evaluate the MFO’s use of technology in managing investments, reporting, and client communication.
- Innovation: Consider whether they are innovative and adaptable to changing financial landscapes and client needs.
10. Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management:
-
- Compliance: Ensure the MFO adheres to regulatory standards and has strong governance practices.
- Risk Management: Evaluate their risk management practices and how they protect clients’ assets.
11. Client References:
-
- References: Ask for and check client references. Speaking with current or former clients can provide valuable insights into the MFO’s performance and client satisfaction.
Bookkeeping is a foundational aspect of financial management, crucial for both U.S. irrevocable trusts and U.S. companies. It involves maintaining accurate and detailed records of all financial transactions, supporting informed decision-making, regulatory compliance, and overall financial health. Here’s an in-depth look at its role in these two contexts:
Key Roles and Responsibilities
1. Accuracy and Reliability
Illustrative Accounting Treatment (Trusts and Single-Member LLCs)
Since single-member LLCs are passthrough entities for income tax purposes, their transactions are typically combined with the trust’s transactions. The end result is typically consolidated financial statements for the trust.
When establishing a trust or making a cash gift to the trust, the transaction is typically recorded as such:
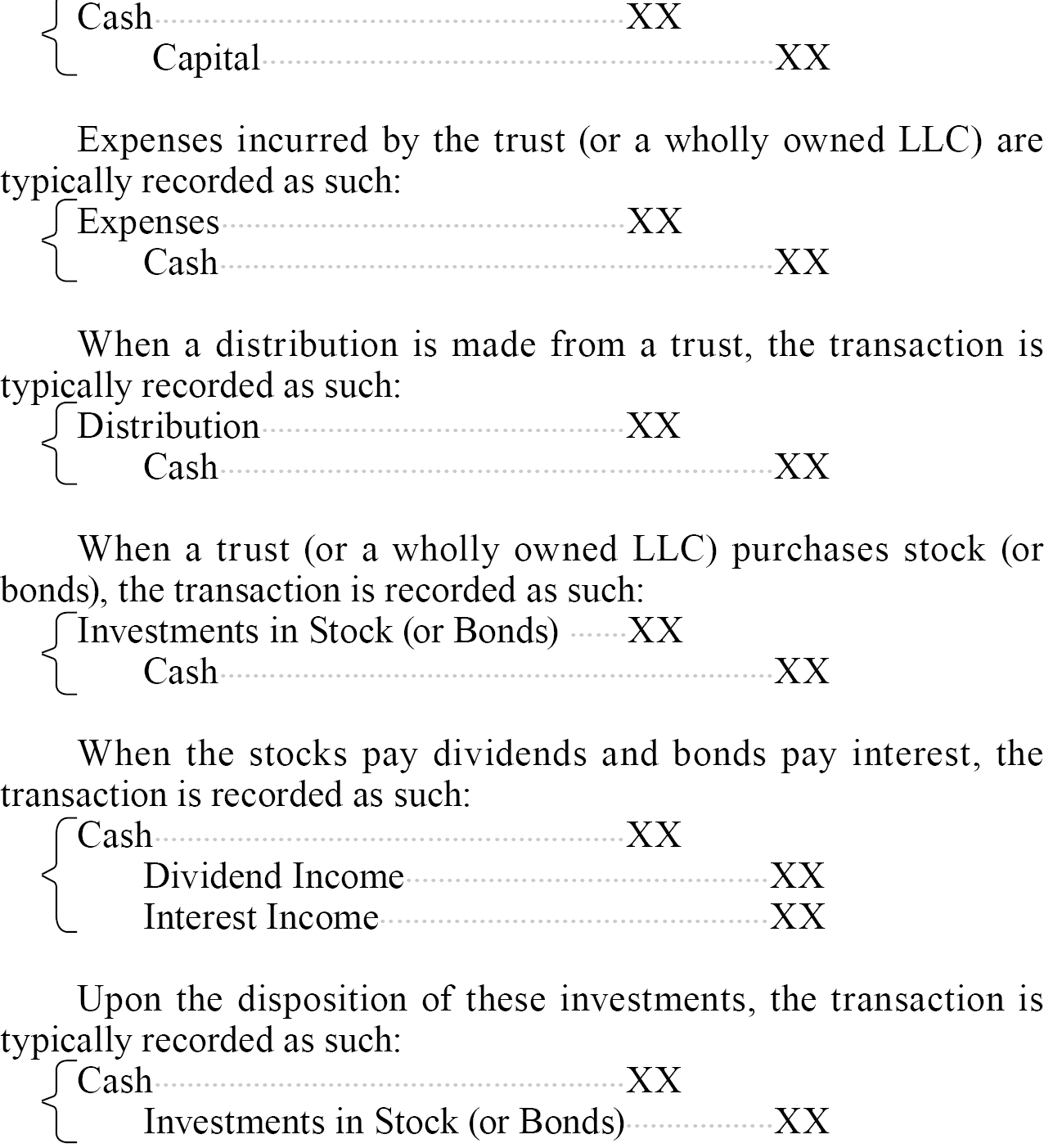
When a trust (or a wholly owned LLC) purchases real estate, the transaction is recorded as such:
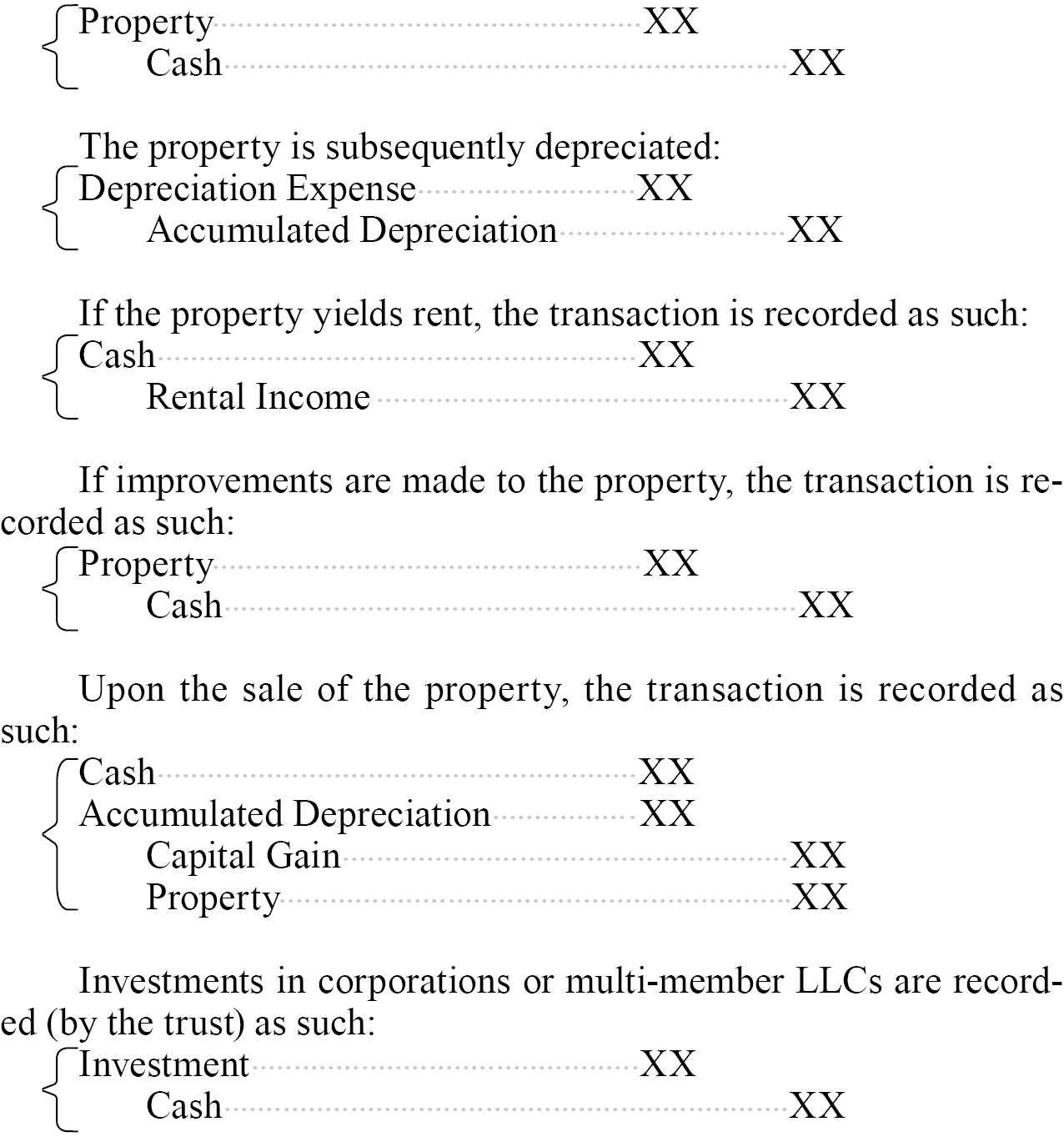
Illustrative Accounting Treatment (Corporations and Multi-Member LLCs)
Corporations (including LLCs that have filed an entity classification election to be taxed as a corporation) in the U.S. are subject to corporate tax rates. LLCs may also be taxed as a partnership for U.S. income tax purposes. As such, unlike single-member LLCs, investments in corporations and multi-member LLCs are generally treated separately from the trust.
When establishing a corporation or making an investment in the corporation, the transaction is typically recorded as such:
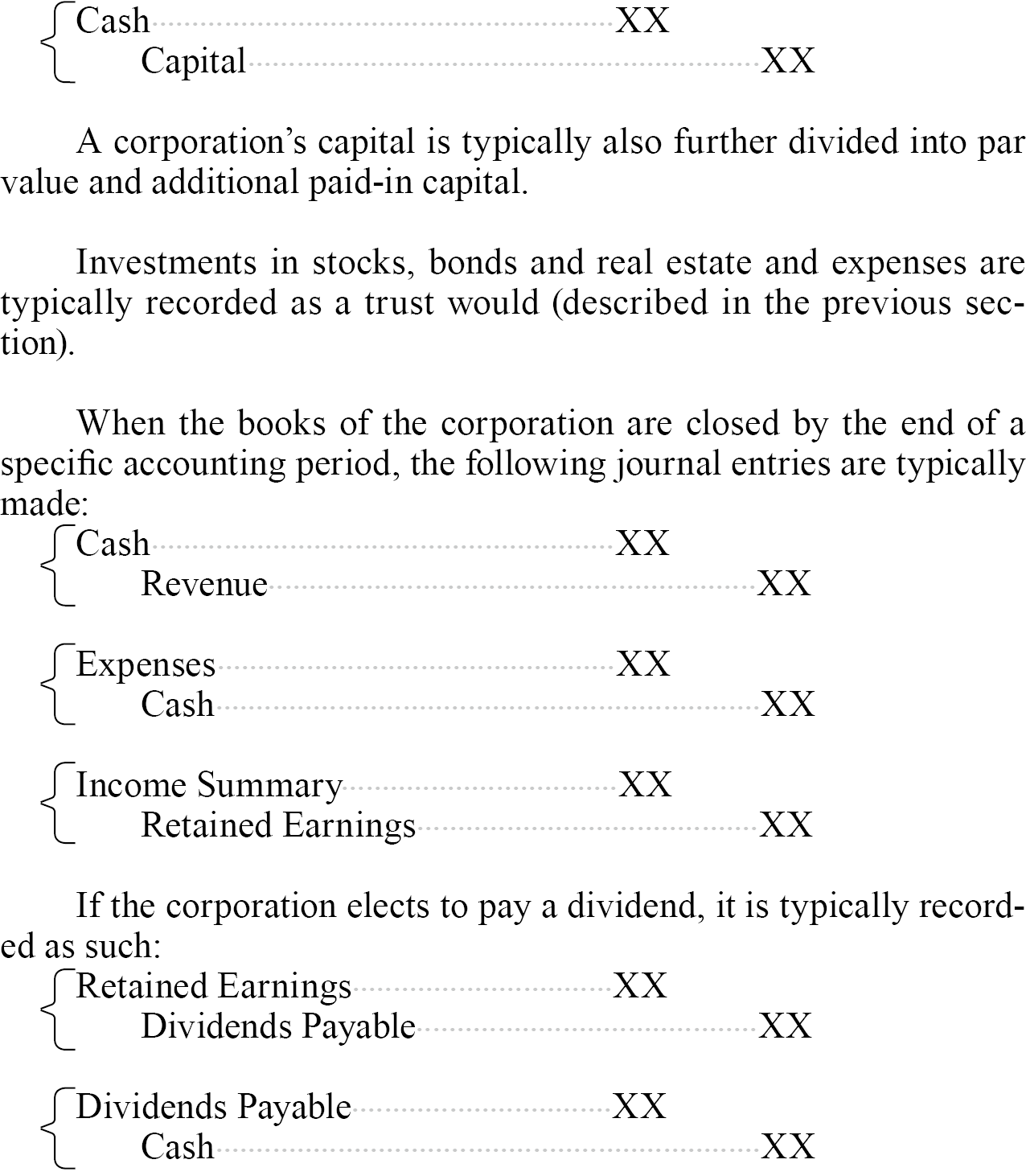
When closing a corporation, the journal entries can be recorded in two primary ways:
1. Transferring assets and liabilities to a newly established corporation or LLC, including any mark-to-market adjustments to the assets.
2. Liquidating the existing corporation.
Below are the relevant ledgers for each scenario:
Scenario 1: Transferring assets and liabilities to a newly established corporation or LLC, including any mark-to-market adjustments to the assets
If the shareholder decides to close the old corporation and transfer the assets and liabilities to the new corporation, the ledger for the old corporation would be recorded as follows:

Scenario 2: Liquidation
If the shareholders decide to end the operation of the corporation, the first step in the accounting treatment will usually involve selling the assets as follows:

After selling the assets, the corporation is obligated to pay off the remaining debt.

After paying off all the remaining debt, if the corporation still has remaining assets (e.g. cash), it shall return the capital to its shareholders.

Illustrative Accounting Treatment (BVI Corporation)
The bookkeeping for a corporation registered in the British Virgin Islands (BVI) is quite similar to that of a US corporation. The most significant discrepancy occurs when the BVI corporation is under the control of a trust. We begin our illustration with a common scenario where a corporation is the shareholder of the BVI corporation. Then we will illustrate the different bookkeeping for the BVI corporation under the trust.
Scenario1: Trust is not the shareholder of the BVI corporation
When a BVI corporation invests in another corporation, the ledger for the BVI corporation is recorded as follows:

Scenario2: Trust is the shareholder of the BVI corporation
When a BVI corporation under a trust invests in another corporation, the ledger for the BVI corporation’s investment is recorded in the same way as in Scenario 1.

However, in Scenario 2, since the BVI corporation adopts the cost method rather than the equity method for booking investment income, it records the investment income only when it receives the cash dividend. Assuming a BVI company receives dividends from a Taiwanese company, Taiwan will withhold 21% tax on dividends paid to foreign shareholders.

Conclusion
Bookkeeping is a vital function in both U.S. irrevocable trusts and companies, underpinning financial health, regulatory compliance, and strategic decision-making. By maintaining accurate and detailed financial records, bookkeepers provide the data necessary for efficient management, regulatory adherence, and business growth. Professional bookkeeping services and advanced accounting software can enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness of this critical function.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
1. Recording Financial Transactions
-
- Income: Documenting all sources of income, including interest, dividends, rental income for trusts, and sales, services, and other revenue streams for companies.
- Expenses: Tracking all expenses, such as administrative costs, management fees, payroll, rent, utilities, and other operational costs.
- Assets and Liabilities: Maintaining detailed records of assets and liabilities, including acquisitions, sales, valuations, and depreciation.
2. Maintaining the General Ledger
-
- Double-Entry System: Using a double-entry accounting system where each transaction affects at least two accounts, ensuring accuracy and balance in the books.
- Account Reconciliation: Regularly reconciling bank statements, credit card statements, and other financial accounts to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Chart of Accounts: Customizing their chart of accounts to fit the specific needs of their business, making it easier to organize and track financial transactions.
3. Producing Financial Statements
-
- Balance Sheet: Summarizing the financial position at a specific point in time, showing assets, liabilities, and equity for companies, or net worth for trusts.
- Income Statement: Detailing financial performance over a period, including revenue, expenses, and profits or losses.
- Cash Flow Statement: Tracking cash inflows and outflows, providing insights into liquidity and cash management.
4. Supporting Tax Compliance
-
- Tax Documentation: Keeping accurate records to support tax filings, including income, deductions, credits, and other relevant data.
- Tax Filings: Assisting in the preparation and timely filing of federal, state, and local tax returns for both trusts and companies.
1. Accuracy and Reliability
-
- Error Reduction: Professional bookkeepers reduce the risk of errors that can lead to financial misstatements or regulatory issues.
- Timely Reporting: Ensuring financial data is recorded promptly, allowing for up-to-date financial reporting and decision-making.
2. Regulatory Compliance
-
- Legal Compliance: Staying current with changes in tax laws, labor laws, and other regulations affecting financial reporting.
3. Operational Efficiency
-
- Streamlined Processes: Implementing efficient bookkeeping processes and leveraging accounting software to automate routine tasks.
Illustrative Accounting Treatment (Trusts and Single-Member LLCs)
Since single-member LLCs are passthrough entities for income tax purposes, their transactions are typically combined with the trust’s transactions. The end result is typically consolidated financial statements for the trust.
When establishing a trust or making a cash gift to the trust, the transaction is typically recorded as such:

When a trust (or a wholly owned LLC) purchases real estate, the transaction is recorded as such:

Illustrative Accounting Treatment (Corporations and Multi-Member LLCs)
Corporations (including LLCs that have filed an entity classification election to be taxed as a corporation) in the U.S. are subject to corporate tax rates. LLCs may also be taxed as a partnership for U.S. income tax purposes. As such, unlike single-member LLCs, investments in corporations and multi-member LLCs are generally treated separately from the trust.
When establishing a corporation or making an investment in the corporation, the transaction is typically recorded as such:

When closing a corporation, the journal entries can be recorded in two primary ways:
1. Transferring assets and liabilities to a newly established corporation or LLC, including any mark-to-market adjustments to the assets.
2. Liquidating the existing corporation.
Below are the relevant ledgers for each scenario:
Scenario 1: Transferring assets and liabilities to a newly established corporation or LLC, including any mark-to-market adjustments to the assets
If the shareholder decides to close the old corporation and transfer the assets and liabilities to the new corporation, the ledger for the old corporation would be recorded as follows:

Scenario 2: Liquidation
If the shareholders decide to end the operation of the corporation, the first step in the accounting treatment will usually involve selling the assets as follows:

After selling the assets, the corporation is obligated to pay off the remaining debt.

After paying off all the remaining debt, if the corporation still has remaining assets (e.g. cash), it shall return the capital to its shareholders.

Illustrative Accounting Treatment (BVI Corporation)
The bookkeeping for a corporation registered in the British Virgin Islands (BVI) is quite similar to that of a US corporation. The most significant discrepancy occurs when the BVI corporation is under the control of a trust. We begin our illustration with a common scenario where a corporation is the shareholder of the BVI corporation. Then we will illustrate the different bookkeeping for the BVI corporation under the trust.
Scenario1: Trust is not the shareholder of the BVI corporation
When a BVI corporation invests in another corporation, the ledger for the BVI corporation is recorded as follows:

Scenario2: Trust is the shareholder of the BVI corporation
When a BVI corporation under a trust invests in another corporation, the ledger for the BVI corporation’s investment is recorded in the same way as in Scenario 1.

However, in Scenario 2, since the BVI corporation adopts the cost method rather than the equity method for booking investment income, it records the investment income only when it receives the cash dividend. Assuming a BVI company receives dividends from a Taiwanese company, Taiwan will withhold 21% tax on dividends paid to foreign shareholders.

Conclusion
Bookkeeping is a vital function in both U.S. irrevocable trusts and companies, underpinning financial health, regulatory compliance, and strategic decision-making. By maintaining accurate and detailed financial records, bookkeepers provide the data necessary for efficient management, regulatory adherence, and business growth. Professional bookkeeping services and advanced accounting software can enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness of this critical function.
Passing on relationships with advisors to the next generation is an important aspect of ensuring continuity and stability in wealth management. Here’s how Wealth Creators can effectively pass on these relationships:
1. Early Introduction and Involvement:
2. Education and Training:
3. Joint Decision-Making:
1. Early Introduction and Involvement:
- Introduce Early: Introduce the next generation to advisors early on. This helps build familiarity and trust.
- Involve in Meetings: Involve the next generation in regular meetings with advisors to understand the financial strategies and decisions being made.
2. Education and Training:
- Financial Education: Provide financial education to the next generation to ensure they understand the basics of wealth management.
- Advisor’s Role: Educate them about the role of each advisor and the value they bring to the table.
3. Joint Decision-Making:
- Collaborative Decisions: Include the next generation in decision-making processes. This can help them feel more engaged and responsible for the family’s wealth.
- Gradual Transition: Gradually transition responsibilities to the next generation with the guidance of advisors.
- Shared Goals: Ensure the next generation understands and aligns with the family’s financial goals and values.
- Trust-Building Activities: Facilitate activities that help build trust between the next generation and the advisors.
- Transparent Discussions: Have open and transparent discussions about the family’s wealth, goals, and the role of advisors.
- Feedback Loop: Create a feedback loop where the next generation can voice their opinions and concerns regarding the advisors and their strategies.
- Formal Agreements: Consider formalizing the relationship through agreements that outline the roles and responsibilities of advisors and the next generation.
- Succession Planning: Develop a clear succession plan that includes the role of advisors in the transition process.
Benefits of passing on advisor relationships to the next generation may include:
1. Continuity and Stability
2. Established Trust
3. Consistent Strategy
While passing on advisor relationships to the next generation can provide continuity, stability, and preserved knowledge, it’s also important to consider the next generation’s preferences and the evolving financial landscape.
Wealth Creators should balance maintaining trusted relationships with the potential benefits of new perspectives and expertise. Ensuring that the next generation is involved, educated, and comfortable with the professional advisors is key to a successful transition.
1. Continuity and Stability
- Seamless Transition: Continuity of advisor relationships can provide stability and ensure a seamless transition of wealth management practices.
- Preserved Knowledge: Advisors who have a long history with the family possess valuable knowledge about the family’s financial history, goals, and values.
2. Established Trust
- Trusted Relationships: Existing advisors have already established trust with the family, which can be difficult to replicate with new advisors.
- Proven Performance: These advisors have a track record of managing the family’s wealth effectively.
3. Consistent Strategy
- Strategic Alignment: Maintaining the same advisors ensures that the financial strategies remain consistent and aligned with the family’s long-term goals.
- Avoiding Disruption: Changing advisors can disrupt financial plans and strategies, leading to potential losses or mismanagement.
While passing on advisor relationships to the next generation can provide continuity, stability, and preserved knowledge, it’s also important to consider the next generation’s preferences and the evolving financial landscape.
Wealth Creators should balance maintaining trusted relationships with the potential benefits of new perspectives and expertise. Ensuring that the next generation is involved, educated, and comfortable with the professional advisors is key to a successful transition.
Wealth Creators often use British Virgin Islands (BVI) companies to distribute their wealth due to the jurisdiction’s favorable legal, tax, and regulatory environment. Here’s how they typically leverage BVI companies for wealth distribution:
By utilizing BVI companies, Wealth Creators can effectively manage and distribute their wealth in a tax-efficient, legally protected, and geographically diversified manner. This strategy supports their objectives of wealth preservation, privacy, and smooth succession across generations.
1. Establishing a BVI Company
-
- Incorporation:
Wealth Creators can incorporate a BVI company quickly and with relative ease. The process is efficient, and the costs are generally lower compared to other jurisdictions.
-
- Anonymity and Confidentiality:
BVI companies offer a high level of privacy. Shareholder information is not publicly accessible, which helps protect the privacy of the Wealth Creator.
2. Holding and Managing Assets
-
- Asset Holding:
BVI companies are often used to hold various types of assets, including real estate, investments, intellectual property, and business interests. This centralizes asset management and provides a clear structure for wealth distribution.
-
- Investment Vehicles:
Wealth Creators can use BVI companies to invest in global markets. The company can hold and manage a diverse portfolio of investments, providing flexibility and efficiency in wealth management.
3. Tax Efficiency
-
- Tax Benefits:
BVI companies benefit from zero corporate tax, no capital gains tax, and no inheritance tax in the jurisdiction. This makes them an attractive vehicle for wealth preservation and growth.
-
- International Tax Planning:
Wealth Creators use BVI companies as part of a broader international tax planning strategy. This can help in minimizing tax liabilities and optimizing the tax efficiency of their wealth distribution plans.
4. Succession Planning
-
- Transfer of Ownership:
Shares in a BVI company can be transferred easily to heirs, ensuring a smooth succession process. This can be done during the Wealth Creator’s lifetime or through provisions in their estate plan.
-
- Avoiding Probate:
By holding assets through a BVI company, Wealth Creators can avoid the lengthy and often costly probate process in other jurisdictions. The company’s shares can be transferred directly to beneficiaries.
5. Legal Protection and Risk Management
-
- Asset Protection:
BVI companies provide strong legal protection for assets. They can safeguard wealth from political instability, economic uncertainties, and legal disputes in other jurisdictions.
-
- Limited Liability:
As with other corporate structures, BVI companies offer limited liability, protecting the personal assets of the Wealth Creator from business liabilities.
6. Flexibility and Control
-
- Control over Assets:
Wealth Creators can retain control over the assets held by the BVI company while setting up mechanisms for their distribution. This includes establishing directorships and management structures that align with their wealth distribution goals.
-
- Flexible Corporate Structures:
BVI companies offer flexible corporate structures that can be tailored to the specific needs of the Wealth Creator. This includes creating multiple classes of shares, implementing shareholders’ agreements, and customizing governance rules.
7. Geographic Diversification
-
- Global Reach:
Using BVI companies allows Wealth Creators to diversify their asset holdings geographically. They can invest in different regions, such as Asia, North America, and Europe, ensuring that their wealth is not concentrated in a single jurisdiction.
8. Estate Planning and Legal Compliance
-
- Estate Planning:
BVI companies can be integrated into comprehensive estate plans that consider the Wealth Creator’s global assets and heirs. This ensures that the distribution of wealth is orderly and aligned with the family’s long-term goals.
-
- Regulatory Compliance:
BVI companies are subject to certain regulatory standards, which helps in maintaining compliance with international laws and reduces the risk of legal challenges.
By utilizing BVI companies, Wealth Creators can effectively manage and distribute their wealth in a tax-efficient, legally protected, and geographically diversified manner. This strategy supports their objectives of wealth preservation, privacy, and smooth succession across generations.
Europe, particularly the European Union (EU), plays a crucial role for cross-border Wealth Creators due to its unique combination of benefits that support global investment, asset protection, and family security. Strategic Advantages include:
1. Freedom of Movement
1. Freedom of Movement
- Visa-Free Travel: EU citizenship or permanent residency allows for unrestricted travel across all 27 EU member states, facilitating business trips and family holidays without visa hassles.
- Residence Flexibility: Wealth Creators can live, work, and study in any EU country, providing numerous options for relocation and business expansion.
- Single Market Access: The EU single market enables seamless business operations across member states, reducing regulatory barriers and tariffs, thus enhancing trade efficiency.
- Diversification: Holding EU citizenship or residency is part of a broader strategy to diversify assets, investments, and residency options.
- Diverse Economic Landscapes: From tech hubs in Germany to financial centers in Luxembourg, the EU offers varied environments for different business ventures.
- Asset Protection: Ensuring wealth is protected in stable jurisdictions with robust legal frameworks.
- Top-Tier Education: Access to high-quality education systems across the EU, often at reduced costs, ensures that families can secure excellent educational opportunities for their children.
- Comprehensive Healthcare: EU countries offer some of the best healthcare services globally, ensuring peace of mind regarding medical needs.
- Favorable Tax Regimes: Several EU countries offer tax incentives for new residents, including exemptions on foreign income or reduced tax rates.
- Double Taxation Treaties: Extensive treaties help in minimizing tax liabilities, making financial planning more efficient.
- High Living Standards: EU countries frequently rank high in global living standards, offering safe, clean, and culturally rich environments.
- Cultural and Social Benefits: Rich cultural heritage and stable political systems enhance the overall living experience.
- Robust Legal Frameworks: The EU’s strong legal protections ensure the safety of assets and investments.
- Stable Political Environment: The predictable political landscape of the EU provides a secure environment for wealth preservation and growth.
- Contingency Planning: Providing a stable alternative residence option in case of instability in the home country.
- Inheritance and Succession: EU citizenship can be passed down, ensuring that the benefits extend to future generations.
- Educational Opportunities for Descendants: Long-term access to top educational institutions for children and grandchildren.
Over the past 30 years, numerous wealth-creating families have built substantial businesses and accumulated significant wealth. As the first generation of wealth creators now faces the crucial task of planning for inheritance, they often hope that their descendants will inherit their wisdom and good fortune, ensuring the longevity of their wealth. As the Chinese proverb says, "Starting a business is difficult, but maintaining it is even harder." Given the increasing geopolitical tensions, stricter tax regulations, and heightened information disclosure requirements, along with the fact that family members often relocate to different countries to meet their personal living needs, family wealth will inevitably extend globally across multiple generations.
To effectively manage investments spread across the globe, high-net-worth family members must be able to move freely between countries. However, increasingly stringent international technology controls and travel restrictions have become significant obstacles for these families. In this context, having EU member state status offers the following advantages:
To effectively manage investments spread across the globe, high-net-worth family members must be able to move freely between countries. However, increasingly stringent international technology controls and travel restrictions have become significant obstacles for these families. In this context, having EU member state status offers the following advantages:
1. Harmonized Legal Framework: The EU provides a unified legal structure for inheritance and estate planning across member states, simplifying asset management and cross-border transfers.
2. European Certificate of Succession: EU citizens benefit from a recognized certificate that facilitates proving heir status or executorship throughout EU nations, streamlining estate administration.
3. Tax Benefits: Bilateral agreements among EU states prevent double taxation on inheritances and estate transfers, ensuring financial savings for beneficiaries.
4. Access to Financial Services: EU residency grants access to diverse financial services and products across member states, enhancing flexibility in managing inherited wealth.
5. Freedom of Movement: EU residents can freely relocate within member states, enabling strategic moves to jurisdictions with favorable tax laws or inheritance regulations.
6. Property Rights Protection: Robust EU regulations safeguard property rights, ensuring efficient management and transfer of inherited assets.
7. Simplified Legal Procedures: Enhanced cooperation among EU states reduces bureaucratic hurdles in legal matters related to inheritance and estate planning, promoting streamlined processes.
Bulgaria offers a particularly attractive program for Cross-Border Wealth Creators. It’s investment requirement, ~€500,000 in an Alternative Investment Fund (AIF), is particularly low compared to other countries in the EU.
In addition, Wealth Creators typically receive their EU Permanent Residency (PR) card within 6 – 8 months and can apply for full Bulgarian Citizenship within 5 years from the initial PR application. Bulgarian citizens enjoy visa-free travel to 142 countries around the world.
Furthermore, Bulgaria’s flat 10% income tax rate only applies to income derived from within the country and the country does not tax its residents on any income derived from outside Bulgaria.
In summary, Europe provides a comprehensive suite of benefits for Cross-Border Wealth Creators, from business and tax advantages to high quality of life and robust legal protections.
Acquiring EU citizenship or permanent residency can significantly enhance personal and family security, business opportunities, and overall wealth management strategies.
Advantages of Obtaining Bulgarian Citizenship
In the past, Asian wealth creators typically chose countries like Portugal, Spain, Greece, and Cyprus for investment immigration to Europe, seldom considering Bulgaria. However, since Bulgaria became a Schengen member state on March 31, 2024, Bulgarian citizens no longer need a passport to travel to most EU countries, Norway, and Switzerland. This enhanced mobility allows Bulgarian citizens to freely move, work, and invest across European countries, gradually making Bulgarian citizenship an option for wealth creators seeking investment immigration. The advantages of investment immigration to Bulgaria are summarized as follows:
An Overview of Bulgaria
Bulgaria is located in southeastern Europe on the Balkan Peninsula, bordered by Romania, Serbia, North Macedonia, Greece, and Turkey, with the eastern coastline along the Black Sea. The capital city, Sofia, serves as the country's political, economic, and cultural hub. Known as the last piece of untouched land in Europe, Bulgaria boasts rich historical landmarks, natural landscapes, unique artistic treasures, and a warm, hospitable culture.
How to Obtain Bulgarian Citizenship & Investment Planning After Obtaining Bulgarian Citizenship
Obtaining a Bulgarian residence permit is the first step towards acquiring EU citizenship. With a Bulgarian residence permit, you can immediately open a personal bank account in Bulgaria, establish a local company, and open corporate bank and investment accounts, laying a solid foundation for future family wealth transfer, tax planning, and legal risk management.
Typically, acquiring Bulgarian residency through investment immigration involves the following steps:
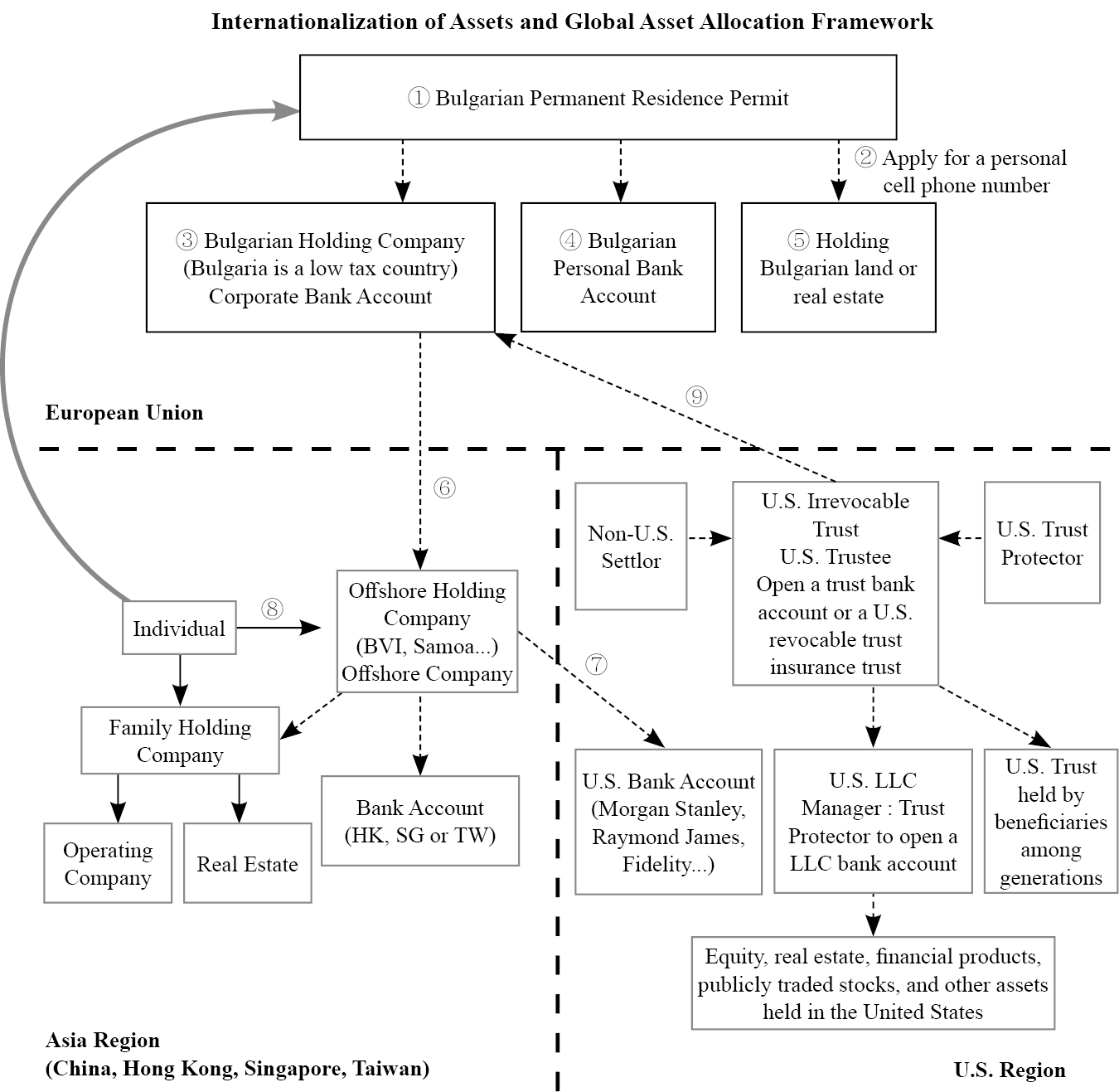
After obtaining Bulgarian citizenship, wealth creators can consider transferring the equity of a Bulgarian holding company into a U.S. irrevocable dynasty trust to further enhance the potential for multigenerational family asset transfer. By combining a U.S. dynasty trust with a Bulgarian holding company, wealth creators can achieve EU citizenship while ensuring that their wealth is protected under U.S. law.
Bulgaria Investment Immigration Program & AIF Investment Immigration Fund
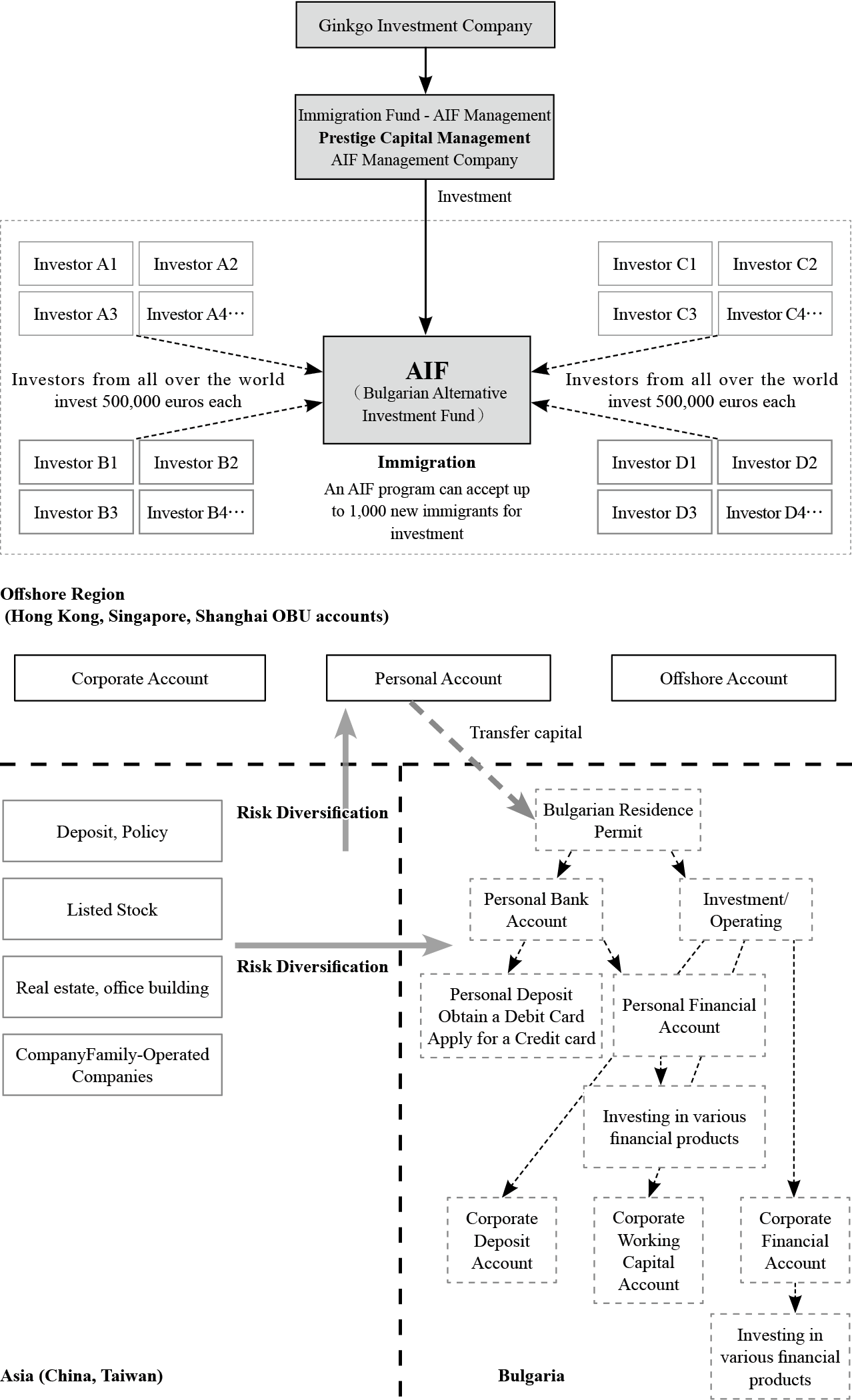
To assist wealth-creating families with investment immigration, Ginkgo Investment Company directly engages local Bulgarian immigration lawyers and introduces the innovative AIF (Alternative Investment Fund) investment immigration service. This service aids clients interested in immigrating to Bulgaria by investing in AIF, facilitating the acquisition of permanent residency and subsequent Bulgarian citizenship.
The operation and investments of AIF must strictly comply with Bulgarian laws. The Bulgarian AIF project primarily invests in Bulgarian company stocks and bonds, aligning with the immigration criteria under Bulgarian citizenship law. Investors participating in the AIF program are required to invest 500,000 euros (approximately 1 million levs). After investing for 6-8 months, they can obtain permanent residency. After 60 months of holding permanent residency, they qualify for Bulgarian citizenship, thereby gaining full EU citizenship rights.
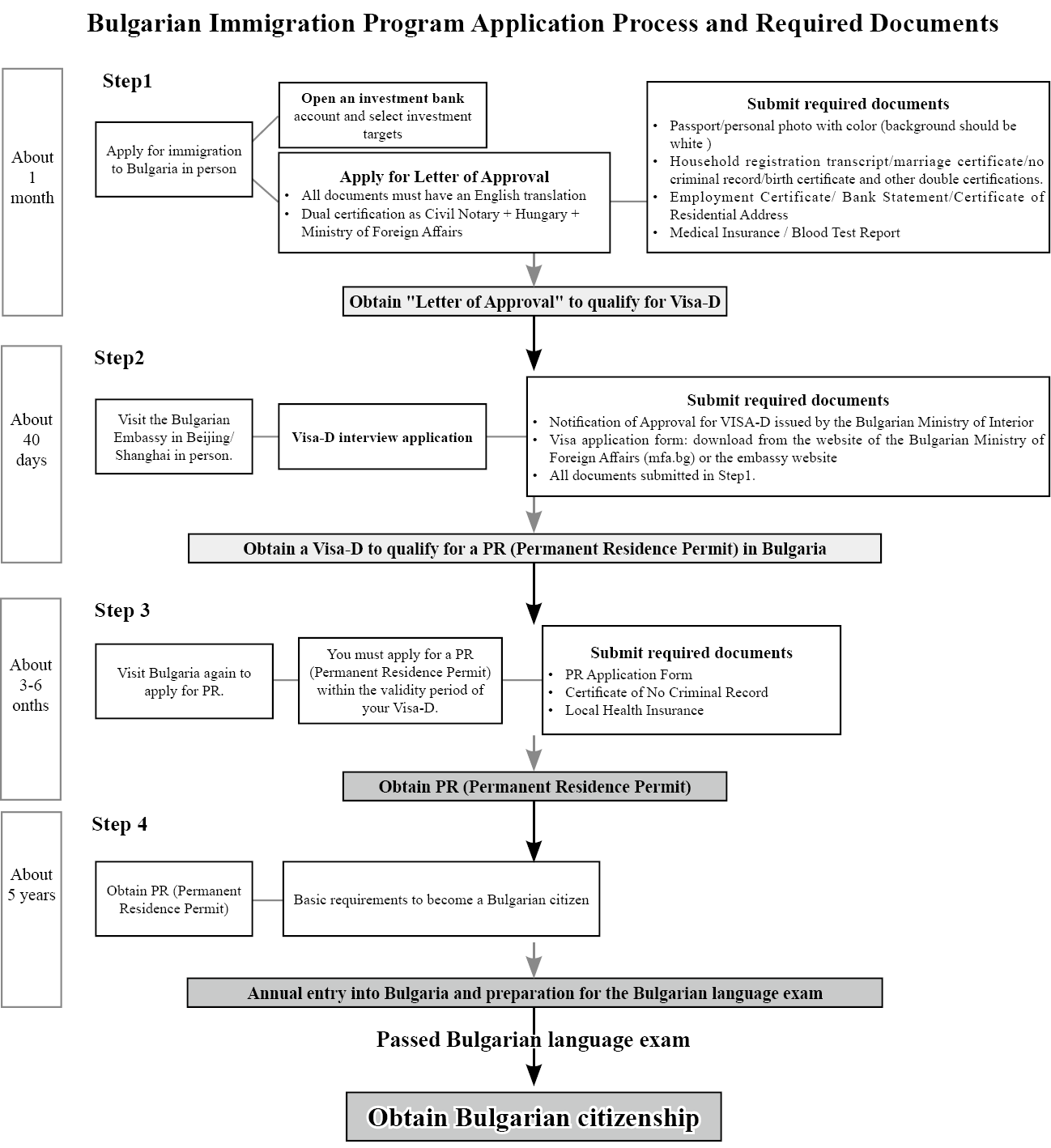
The process of immigration and obtaining Permanent Residency (PR)
Step 1 : Apply for Immigration to Bulgaria in person
Step 2 : Visit the Bulgarian Embassy in Beijing / Shanghai in person
Step 3 : Visit Bulgaria again to appy for PR
Step 4 : Obtain PR (Permanent Residence Permit)
Step 5: Pass the Bulgarian language exam and obtain Bulgarian citizenship and passport
In addition, Wealth Creators typically receive their EU Permanent Residency (PR) card within 6 – 8 months and can apply for full Bulgarian Citizenship within 5 years from the initial PR application. Bulgarian citizens enjoy visa-free travel to 142 countries around the world.
Furthermore, Bulgaria’s flat 10% income tax rate only applies to income derived from within the country and the country does not tax its residents on any income derived from outside Bulgaria.
In summary, Europe provides a comprehensive suite of benefits for Cross-Border Wealth Creators, from business and tax advantages to high quality of life and robust legal protections.
Acquiring EU citizenship or permanent residency can significantly enhance personal and family security, business opportunities, and overall wealth management strategies.
Advantages of Obtaining Bulgarian Citizenship
In the past, Asian wealth creators typically chose countries like Portugal, Spain, Greece, and Cyprus for investment immigration to Europe, seldom considering Bulgaria. However, since Bulgaria became a Schengen member state on March 31, 2024, Bulgarian citizens no longer need a passport to travel to most EU countries, Norway, and Switzerland. This enhanced mobility allows Bulgarian citizens to freely move, work, and invest across European countries, gradually making Bulgarian citizenship an option for wealth creators seeking investment immigration. The advantages of investment immigration to Bulgaria are summarized as follows:
1. Fast Track to Residency and Citizenship: Bulgaria offers a rapid pathway to residency and citizenship, particularly through investment immigration programs. This allows foreign nationals to obtain permanent residency in a short period and apply for citizenship within a relatively short time frame.
2. Low Cost of Living: Compared to living in the United States, the cost of living in Bulgaria is relatively low, including expenses for housing, food, transportation, and other daily necessities, making it an ideal choice for economic immigration to Europe.
3. Favorable Tax System: Bulgaria has one of the lowest tax rates in Europe, with the lowest personal and corporate income tax rates in the EU. This provides an attractive tax environment for entrepreneurs and high-income individuals. Bulgaria’s personal income tax rate is only 10%, the lowest in the EU. Additionally, those who reside in Bulgaria for less than 183 days are considered non-tax residents and are exempt from personal income tax. For dividend income, Bulgaria imposes a 5% tax, but for EU citizens, the dividend tax rate is 0%. Bulgaria has also signed numerous tax treaties with other countries (e.g., China-Bulgaria Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement) to prevent double taxation and promote foreign investment.
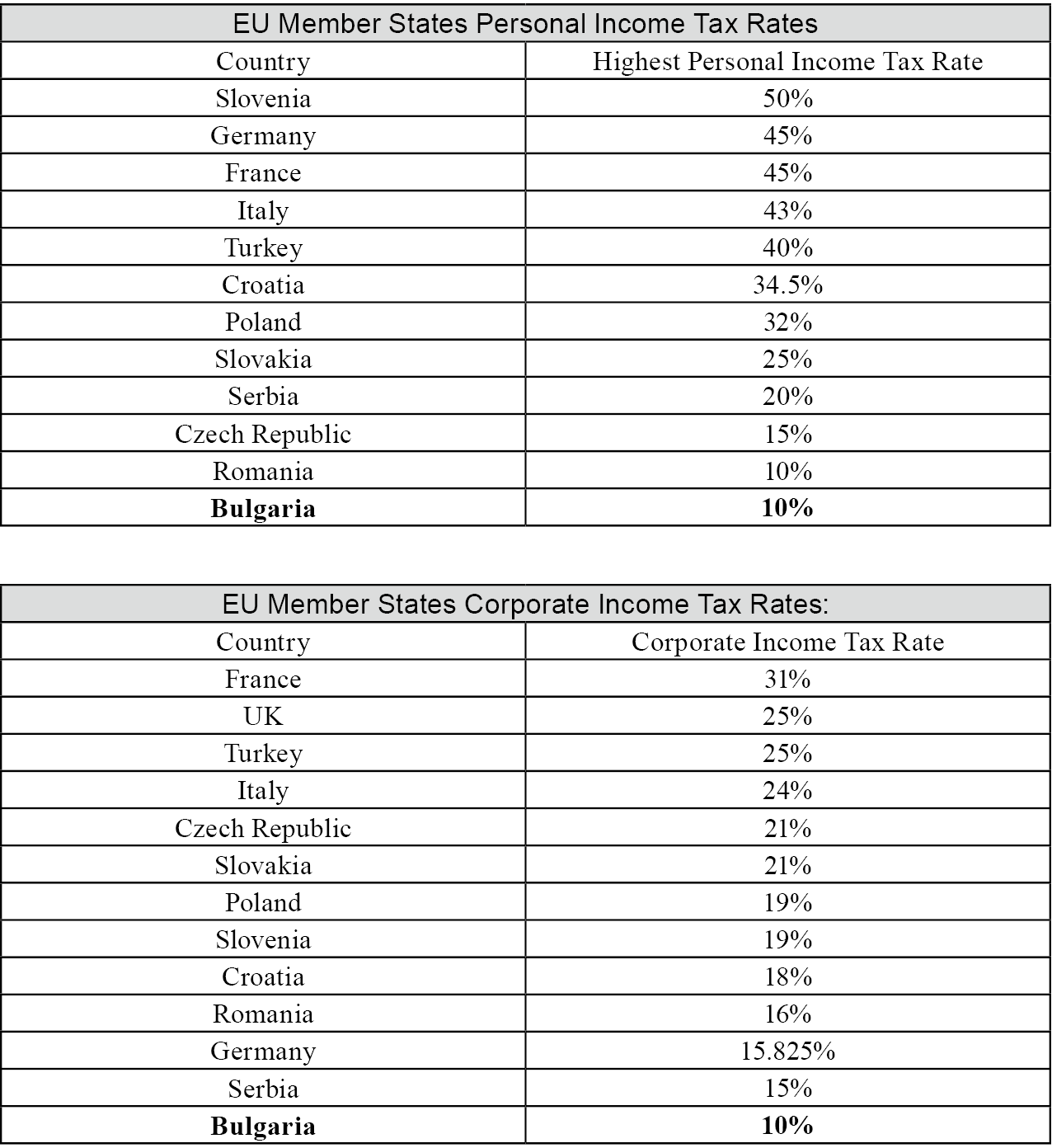
4. EU Member State Status: As an EU member state, Bulgarian citizens enjoy the right to freely travel, work, study, and receive local health insurance benefits (e.g., can apply for the European Health Insurance Card, EHIC) in other EU countries. This provides immigrants with the flexibility and opportunities to live across the EU in the future. Furthermore, Bulgarian nationality law supports the acquisition of Bulgarian nationality for family members of its citizens without age restrictions, allowing wealth creators to consider family-based immigration.
5. Visa-Free Access to Multiple Countries: Holding a Bulgarian passport allows visa-free travel not only within Schengen countries without passport checks but also to up to 142 countries, including the UK and Canada.
6. Pleasant Natural Environment and Climate: Bulgaria boasts beautiful natural scenery, such as magnificent mountains and the Black Sea coast, along with a pleasant climate, making it an ideal place to live and enjoy life.
These advantages make Bulgarian citizenship a compelling choice for those considering investment immigration, offering economic benefits, increased mobility, and a favorable living environment.
4. EU Member State Status: As an EU member state, Bulgarian citizens enjoy the right to freely travel, work, study, and receive local health insurance benefits (e.g., can apply for the European Health Insurance Card, EHIC) in other EU countries. This provides immigrants with the flexibility and opportunities to live across the EU in the future. Furthermore, Bulgarian nationality law supports the acquisition of Bulgarian nationality for family members of its citizens without age restrictions, allowing wealth creators to consider family-based immigration.
5. Visa-Free Access to Multiple Countries: Holding a Bulgarian passport allows visa-free travel not only within Schengen countries without passport checks but also to up to 142 countries, including the UK and Canada.
6. Pleasant Natural Environment and Climate: Bulgaria boasts beautiful natural scenery, such as magnificent mountains and the Black Sea coast, along with a pleasant climate, making it an ideal place to live and enjoy life.
An Overview of Bulgaria
Bulgaria is located in southeastern Europe on the Balkan Peninsula, bordered by Romania, Serbia, North Macedonia, Greece, and Turkey, with the eastern coastline along the Black Sea. The capital city, Sofia, serves as the country's political, economic, and cultural hub. Known as the last piece of untouched land in Europe, Bulgaria boasts rich historical landmarks, natural landscapes, unique artistic treasures, and a warm, hospitable culture.
1. Religion: Bulgaria is predominantly Eastern Orthodox (82.6%), with a significant Muslim minority (12.2%). The country upholds religious freedom, allowing its citizens to practice their faith freely.
2. Language: The official language is Bulgarian, with English widely spoken as a common second language.
3. Climate: Bulgaria experiences a temperate continental climate. The eastern regions are influenced by the Black Sea, and the southern regions by the Mediterranean, resulting in a Mediterranean-type climate. The average annual temperature is about 10.5°C, with January being the coldest month (average temperatures between -1°C and 2°C) and July the warmest (average temperatures between 20°C and 25°C). The annual average precipitation is around 450 millimeters.
4. Population and Ethnicity: Bulgaria has a total population of approximately 6.9 million people. The ethnic composition is primarily Bulgarian (84%), with a significant Turkish minority (8.8%), and the remaining population consisting of various other ethnic groups.
5. Economy: Bulgaria's economy is primarily based on agriculture, with roses, yogurt, and wine being internationally renowned products. The national currency is the Lev (BGN), which has maintained a stable exchange rate, currently pegged at approximately 1 Euro = 1.95583 Lev. Following the pandemic, Bulgaria has sustained a stable economic growth rate, with a 3.4% growth in 2022 and an impressive 7.6% growth in 2021, indicating recovery from the impact of COVID-19. Additionally, Bulgaria's stable political and investment environment continues to attract numerous foreign investors and entrepreneurs.
How to Obtain Bulgarian Citizenship & Investment Planning After Obtaining Bulgarian Citizenship
Obtaining a Bulgarian residence permit is the first step towards acquiring EU citizenship. With a Bulgarian residence permit, you can immediately open a personal bank account in Bulgaria, establish a local company, and open corporate bank and investment accounts, laying a solid foundation for future family wealth transfer, tax planning, and legal risk management.
Typically, acquiring Bulgarian residency through investment immigration involves the following steps:
1. Invest in the Bulgarian Immigration Fund: Invest 500,000 euros to obtain a permanent residence permit in Bulgaria.
2. Get a Local Mobile Phone: Apply for a Bulgarian mobile phone, which serves as a basic tool for opening personal or company bank accounts and activating banking apps.
3. Establish a Local Company: Set up a local Bulgarian company, whether it be an investment company, operational company, or holding company.
4. Open a Local Personal Bank Account: Open a personal bank account in Bulgaria.
5. Acquire Real Estate: As a permanent resident, you can hold local land ownership or real estate in Bulgaria.
6. Hold Offshore Holding Company: Hold overseas holding companies under Bulgarian investment company name.
7. Open Investment Accounts in the US: Open investment accounts in the US investment banks in the name of the offshore holding company.
8. Internationalize Asian Equity Holdings: Transfer personal equity holdings in Asia to the offshore holding company.
9. Transfer Bulgarian Holding Company Equity to a US Family Trust: Transfer the equity of the Bulgarian holding company to a US family trust to achieve cross-border inheritance, asset protection, and tax planning purposes.

After obtaining Bulgarian citizenship, wealth creators can consider transferring the equity of a Bulgarian holding company into a U.S. irrevocable dynasty trust to further enhance the potential for multigenerational family asset transfer. By combining a U.S. dynasty trust with a Bulgarian holding company, wealth creators can achieve EU citizenship while ensuring that their wealth is protected under U.S. law.
Bulgaria Investment Immigration Program & AIF Investment Immigration Fund
To assist wealth-creating families with investment immigration, Ginkgo Investment Company directly engages local Bulgarian immigration lawyers and introduces the innovative AIF (Alternative Investment Fund) investment immigration service. This service aids clients interested in immigrating to Bulgaria by investing in AIF, facilitating the acquisition of permanent residency and subsequent Bulgarian citizenship.
The operation and investments of AIF must strictly comply with Bulgarian laws. The Bulgarian AIF project primarily invests in Bulgarian company stocks and bonds, aligning with the immigration criteria under Bulgarian citizenship law. Investors participating in the AIF program are required to invest 500,000 euros (approximately 1 million levs). After investing for 6-8 months, they can obtain permanent residency. After 60 months of holding permanent residency, they qualify for Bulgarian citizenship, thereby gaining full EU citizenship rights.

The process of immigration and obtaining Permanent Residency (PR)
Step 1 : Apply for Immigration to Bulgaria in person
Step 2 : Visit the Bulgarian Embassy in Beijing / Shanghai in person
Step 3 : Visit Bulgaria again to appy for PR
Step 4 : Obtain PR (Permanent Residence Permit)
Step 5: Pass the Bulgarian language exam and obtain Bulgarian citizenship and passport

1. Research Bulgaria
4. Hire a professional immigration consulting law firm to prepare applicable forms. The law firm typically provides the following services:
6. Invest €500,000 into a government-approved Alternative Investment Fund by transferring funds from the investor’s personal account (typically in the U.S., Hong Kong or Singapore).
7. Apply for Pre-Approval and Visa-D from the Bulgaria Ministry of Foreign Affairs:
- Due Diligence: Conduct thorough due diligence on the program, investment opportunities, and the agents or firms assisting with the process.
- Legal Advice: Seek comprehensive legal and financial advice to understand all implications, including tax obligations and compliance requirements.
- Reputable Agents: Use reputable and certified advisors who have a proven track record in managing citizenship by investment applications.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of any changes in the political and regulatory landscape of the chosen country and the EU as a whole.
- Passport and personal photos with a white background.
- Household registration transcript.
- Marriage certificate (if applicable).
- No criminal record certificate.
- Birth certificates.
- Employment certificate.
- Bank statements.
- Certificate of residential address.
- Medical insurance and blood test report.
4. Hire a professional immigration consulting law firm to prepare applicable forms. The law firm typically provides the following services:
- Advises on and prepares supporting documentation for the client’s pre-approval process.
- Obtains a certificate confirming the client’s eligible investment from the competent authority.
- Advises on and prepares supporting documentation for the client’s visa and permanent residence applications, guiding the client through these processes.
- Liaises with Bulgarian authorities following the issuance of permanent residence approval and assists with local population register compliance.
- Organizes and accompanies the client to their Permanent Residence Permit issuance appointment, assisting with the issuance and collection of the Permanent Residence Permit.
- Advises on and prepares supporting documentation for the spouse’s and children’s visa and permanent residence applications, guiding them through these processes.
6. Invest €500,000 into a government-approved Alternative Investment Fund by transferring funds from the investor’s personal account (typically in the U.S., Hong Kong or Singapore).
7. Apply for Pre-Approval and Visa-D from the Bulgaria Ministry of Foreign Affairs:
- Visit a Bulgarian Consulate in Los Angeles or Washington D.C. in the U.S. or Shanghai or Beijing in China.
- Submit applicable documents and forms, including the Visa-D Application.
- Receive Preliminary Letter of Approval and Visa-D.
- Visit Bulgaria: Travel to Bulgaria to apply for the permanent residence permit within the validity period of the Visa-D.
- Submit required documents including:
- PR application form.
- Certificate of no criminal record.
- Local health insurance.
- Obtain Permanent Residence Permit: Complete the application process.
- Maintain Bulgarian Residency: Ensure annual entry into Bulgaria and maintain a Bulgarian residential address.
- Apply for Citizenship: After keeping Permanent Residence status for five years, Wealth Creators can apply for Bulgarian citizenship.
- Obtain a Local Cell Phone Number: Necessary for communicating and opening bank accounts.
- Open a Personal Bank Account: Required for financial transactions in Bulgaria and in the EU.
- Establish an operating or investment company in Bulgaria.
- Open corporate bank or investment account(s).

