Publications
U.S. Trust and Estate Planning 美國信託規劃實務(英文部分)
Chapter 4 Relevant U.S. Tax Forms for U.S. Trusts & Individuals
2. Form 3520
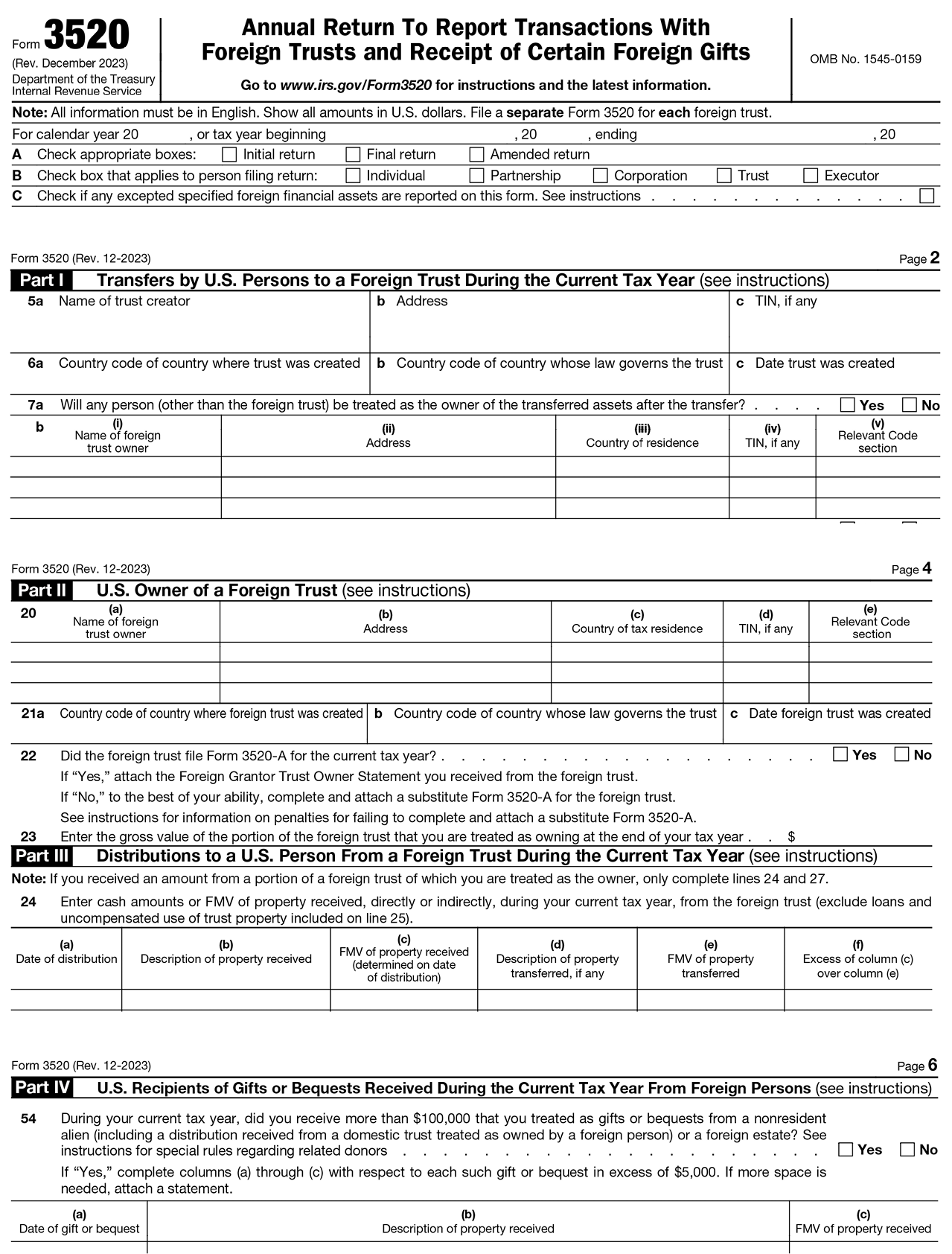
A gift is subject to U.S. gift tax when made by a foreign donor (who would pay the tax) only if it is a gift of tangible personal property physically situated in the United States. However, even if a gift does not give rise to U.S. federal income tax or gift tax liability, if a U.S. person receives gifts from a foreign person, the U.S. person may be required to report such gifts.
More specifically, if the value of the aggregate foreign gifts received by a U.S. person during any tax year exceeds a certain threshold, the U.S. person is required to report certain information on such foreign gifts on Form 3520. For this purpose, a “foreign gift” is any amount received from a foreign person that the recipient treats as a gift or bequest. Thus, foreign gifts could include gifts of cash or personal property (such as cars, art, or furniture), as well as gifts of residential real property. In addition, foreign gifts could include payments made by the foreign person on behalf of the U.S. person.
With respect to the threshold, a U.S. person must report the receipt of gifts from a foreign individual or foreign estate if the aggregate amount of gifts from that foreign individual or foreign estate exceeds $100,000 during the tax year. Form 3520 further requires that the U.S. person separately identify each gift in excess of $5,000 by providing the date of the gift, a description of the property received, and the fair market value (FMV) of the property received.
For individuals receiving gifts from non-U.S. persons totaling more than $100,000 or Foreign Trusts, Form 3520 is required. Certain trusts may also be required to file Form 3520 upon receiving gifts from non-U.S. persons.
Since the penalties for failing to file Form 3520 are especially heavy, you should pay special attention to ensure that the form is filed both timely and accurately. Those who fail to report foreign gifts may be liable for up to 25% of the amounts received. Penalties for individuals who received distributions from Foreign Trusts may be liable for 35% of the amounts received.

